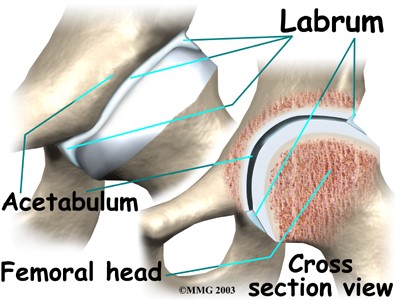
Labral injury of the Hip Joint
The labrum is a tough fibro-cartilaginous ring of tissue that surrounds the bony hip socket. Its function is to deepen the socket, provide stability of the joint and assist in joint lubrication and sensation.
What are the symptoms of labral injury?
Patients with acetabular labral tears commonly experience groin pain, which is often made worse with physical activity and positions where the hip is bent, such as deep squatting or rising from a low chair. The symptoms may have been present for a long time, and thought to represent ‘recurrent groin sprains’. Some patients experience ‘mechanical’ symptoms such as catching or unpredictable ‘weakness’ of the hip joint.
What treatment is available for labral injury?
After making the diagnosis which is usually confirmed with clinical examination and MRI scan, the labrum can be repaired via hip arthroscopy (keyhole surgery).
If there is a structural reason why the labrum is torn such as impingement, then this should also be addressed to prevent future damage.