Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip (DDH)
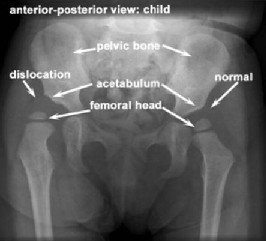
This condition, which also goes by the name of Congenital Dislocation Of The Hip (CDH) and Hip Dysplasia, describes a spectrum of disease due to failure of normal formation of the hip.
This can range from a hip that is subluxatable (unstable when stressed) due to slight shallowness of the hip socket, to one that is completely dislocated. The term CDH implied that the hip was dislocated at birth in these children, but this term has been replaced by DDH as the hip can be in joint at birth but gradually move out of the joint with time if the condition is not diagnosed promptly and treated early.
Screening for DDH
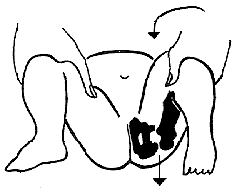
Barlows test – stress test to see if hip is dislocatable
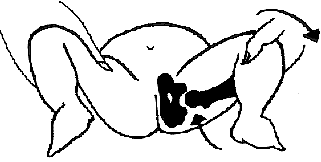
Ortolani’s test which shows a hip reducing
Every newborn child has a hip examination just after birth before leaving hospital. There should also be a clinical examination at about 6 weeks performed by the GP.
Unfortunately, clinical examination, even in the best hands, can only detect those hips that are dislocated or very unstable. It does not exclude dysplasia which can then lead to dislocation at a later date. This is why hip ultrasound is by far the best diagnostic test and this should be combined with expert clinical examination.
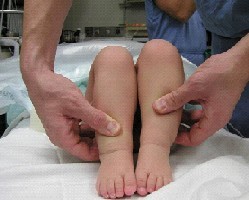
Short right leg raising suspicion of right hip dislocation
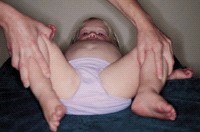
Reduced abduction of right hip
In an older child, it may be possible to see a difference in leg lengths if a hip is dislocated.
This will be combined with a decrease in hip abduction (movement of the hip to the side) and by the time the child is walking then there will be an obvious limp present.
Treatment
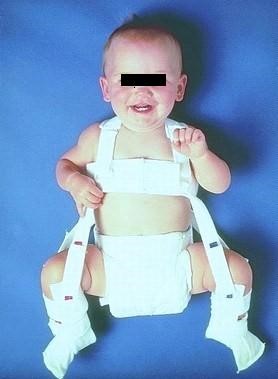
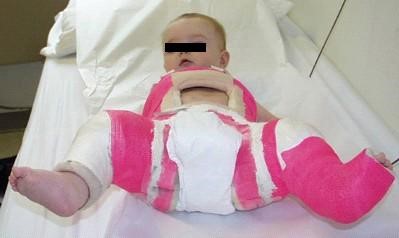
Once the diagnosis if DDH has been made, the treatment will depend on the age of the child and the degree of instability. If the ultrasound shows that the hip is subluxating, dislocated, or that the acetabulum is shallow (decreased femoral head coverage), the initial treatment may consist of a Pavlik harness. The Pavlik harness is often used as the initial treatment of hip dysplasia in infants. It is a soft dynamic brace that maintains the hip in flexion (knee up towards the head) and abduction (knee away from the centerline). This position maintains the proper position of the femoral head and allows for “tightening up” of the ligamentous structures as well as for stimulation of normal formation and deepening of the hip socket.